PAVLOS PAVLAKIS UROLOGY
Robotic
Surgery
Experience the precision of advanced robotic surgery — accuracy, safety, and faster recovery for every patient.

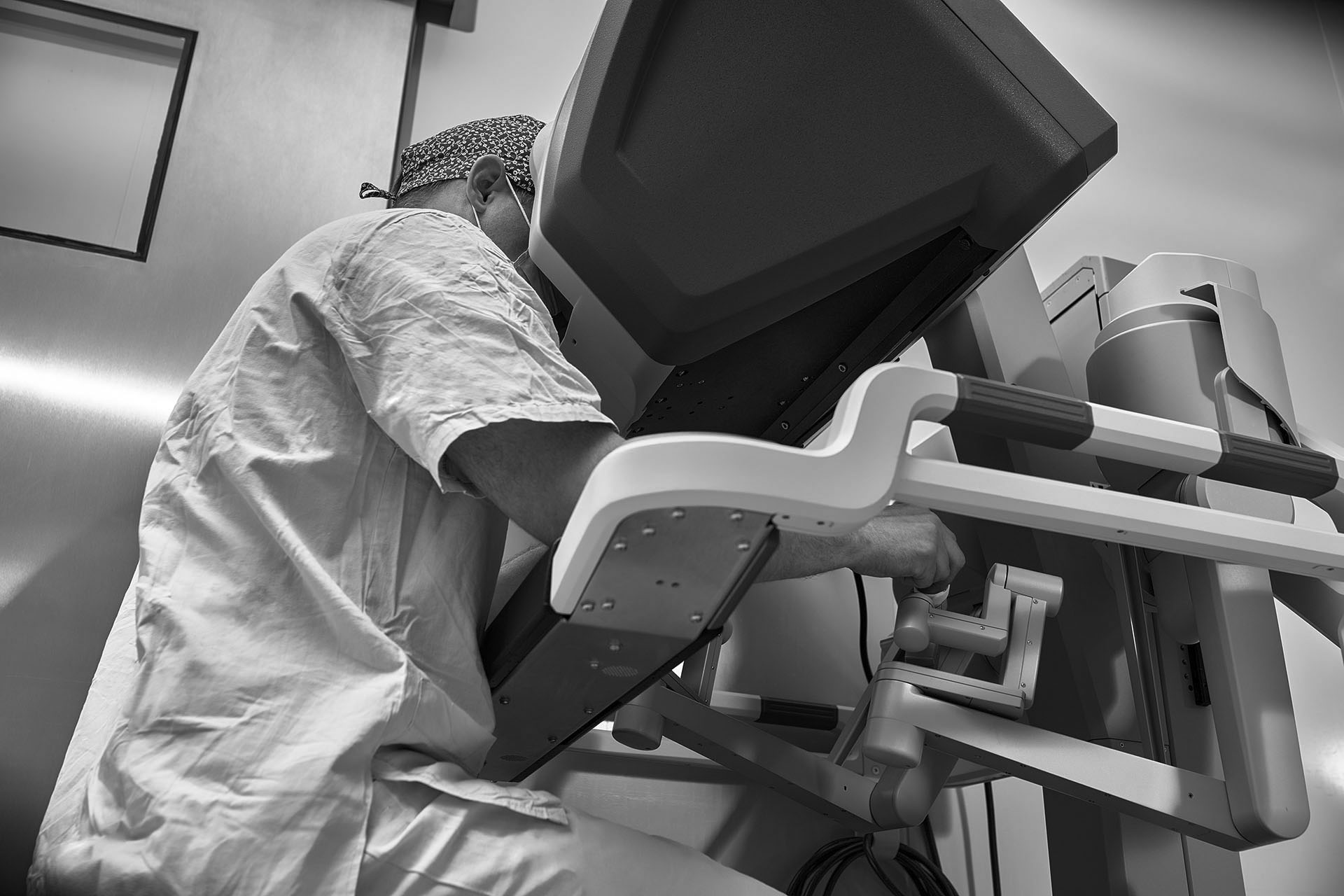
Introduction
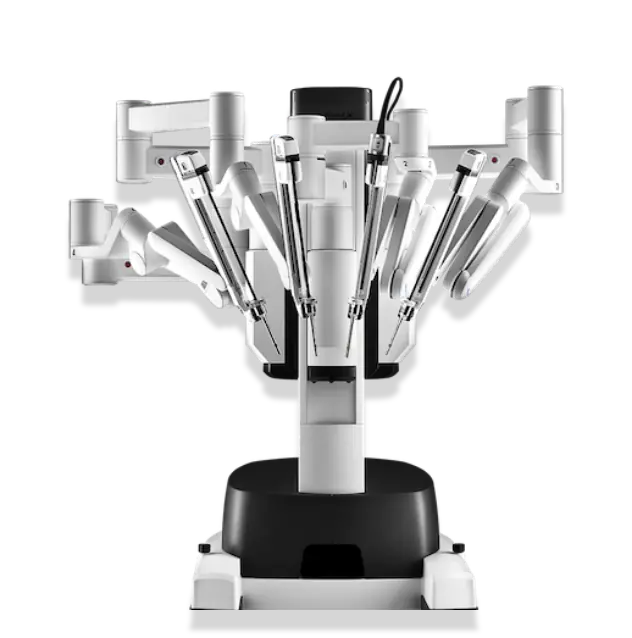
Robotic surgery is the most advanced development in urological surgery. It is a minimally invasive technique that allows the surgeon to perform complex procedures with great precision, using the da Vinci robotic system. Through small incisions, the surgeon controls robotic instruments with complete stability and a 3D high-definition view. The result is less pain, minimal blood loss, and a faster recovery for the patient.
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
- Smaller incisions and better cosmetic result
- Minimal blood loss
- Less postoperative pain
- Faster recovery and return to daily activities
- Greater precision and safety during surgery
- Lower risk of complications
Procedures Performed
- Robotic Prostatectomy
- Robotic Cystectomy
- Robotic Nephrectomy
- Andrological and pelvic floor procedures

"Robotic Surgery,
Performed Procedures"
Robotic surgery is an advanced surgical method that utilizes robotic systems to perform procedures with high precision and accuracy. The procedures that can be conducted through robotic surgery include:
Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer:
“Removal of the prostate and nearby lymph nodes for the treatment of prostate cancer.”
Lymph node dissection for staging of prostate cancer:
Removal of lymph nodes around the prostate to assess the spread of cancer.
Radical nephrectomy for tumor or simple for non-functional kidney:
Removal of an entire kidney for the treatment of malignant tumor or a non-functional kidney.
Partial nephrectomy for tumor or simple for non-functional kidney:
Removal of part of the kidney for the treatment of tumor or a non-functional kidney.
Removal of renal cysts:
Removal of cysts formed in the kidney.
Radical nephroureterectomy for tumors of the ureter or renal pelvis:
Removal of the ureter and renal pelvis to treat malignant tumor.
Αdrenalectomy for benign or malignant tumors:
Removal of the adrenal gland to treat tumors.
Ureterolithotomy:
Surgical procedure for the removal of large stones from the ureter that cannot be treated endoscopically.
Radical retroperitoneal lymph node dissection for advanced testicular tumors:
Removal of lymph nodes in the testicular region to treat advanced cancer.
Radical cystectomy for malignant tumor:
Removal of the entire bladder to treat malignant tumor.
Pyeloplasty for narrowing of the pelvi-ureteric junction:
Surgical procedure to expand or open the pelvi-ureteric junction.
Simple nephrectomy for small or non-functional kidney:
Removal of a small or non-functional kidney.

Robotic
Prostatectomy
Robotic prostatectomy is the most advanced and precise method for removing the prostate in cases of cancer. Using the Da Vinci robotic system, the surgeon performs the procedure with exceptional precision through small incisions. Benefits for the patient include minimal blood loss, less pain, shorter hospital stay, and better preservation of continence and sexual function.
Robotic
Cystectomy
Robotic cystectomy is performed in cases of invasive bladder cancer. Using a robotic system, the bladder is removed with great precision and minimal blood loss. In the same operation, a neobladder can be created from a segment of the intestine, allowing natural urination. The technique offers reduced surgical trauma, faster recovery, and excellent functional outcomes.

